CommCare HQ Platform Overview
The major functional components are:
Application Building and Content Management
Application Data Layer
Tenant Management
Analytics and Usage
Messaging Layer
Integration
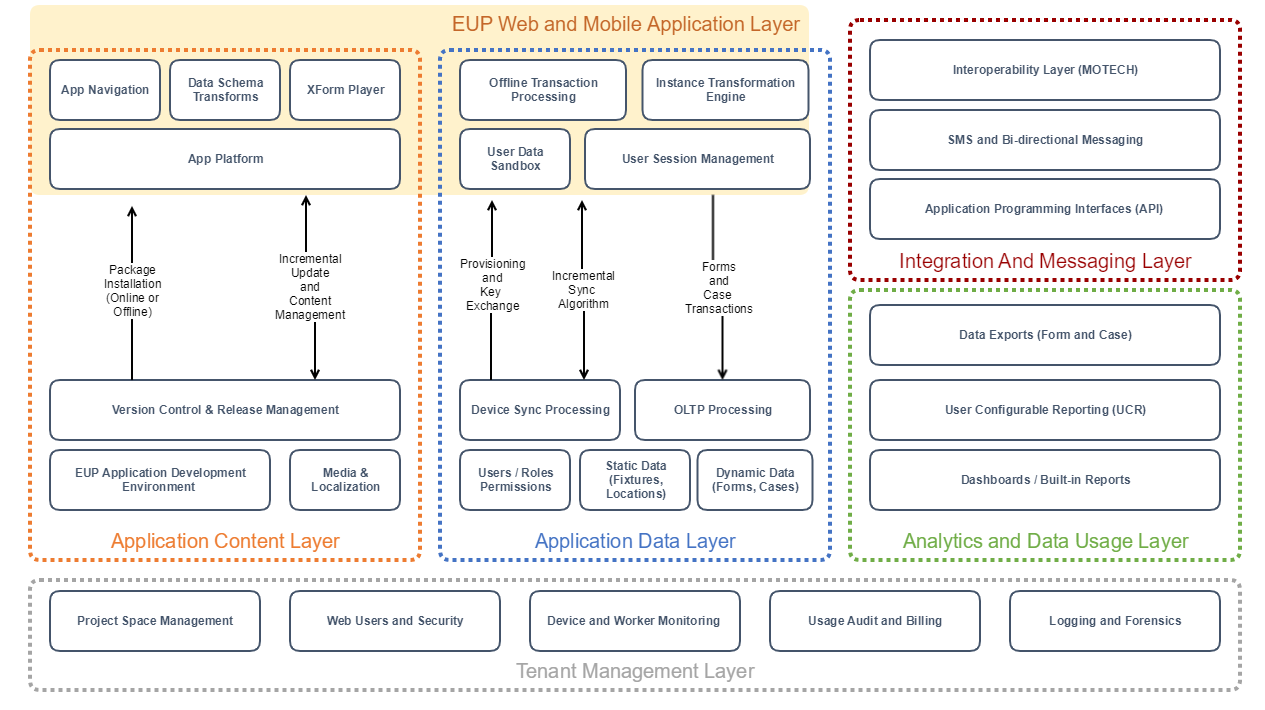
Application Content Layer
Application Building and Deployment Management
The Application Builder provides an interface for users to create and structure an application’s content and workflow. Questions can be added by type (text, integer, multiple answer, date, etc.) and logic conditions can be applied to determine whether the question should be displayed or if the answer is valid.
This environment also provides critical support for detailed management of content releases. CommCare’s deployment management provides a staging-to-deploy pipeline, profile-based releases for different regions, and supports incremental rollout and distribution for different regions.
Android Mobile App Runner and Web App Engine
Applications developed in the end user programming (EUP) content builder are deployed to users and then executed within the CommCare application engine, which is built on a shared Java codebase. The application configurations can be run on both a native Android client and a Spring web client, to allow access for users in the field as well as those accessing the application from a computer on the web.
Application Data Layer
Data Management
There are two data models that underpin the CommCare data model:
Form A form is the basic building block of Applications. Forms are represented as XForms (XML Forms) which contain data, logic and rules. Users interact with forms on the mobile device to capture data and perform logic. This data is then sent back to CommCare as a form submission which is an XML document containing only the data portion of the XForm.
Forms may include case blocks which can be used to create, update and close cases.
Case Cases are used to track interactions with objects, often people. Cases provide longitudinal records which can track the ongoing interactions with a case through form submissions and facilitate the complex sharding and reconciliation required from synchronizing offline clients.
Each case has a type, such as “patient”, “contact”, “household” which distinguishes it from cases of other types. Cases may also be structured in a hierarchy using uni-directional relationships between cases.
The full specification for cases can be found here.
Transaction Processing
CommCare provides a transaction processing layer which acts as the first step in the underlying data and storage pipeline. This layer manages the horizontal workload of the mobile and web applications submitting forms, which are archived into a chunked object storage, and extracts the transactional ‘case’ logic which is used to facilitate data synchronization through more live storage in the table based storage layer. The transaction processor then appropriately queues transactions into the real time data pipeline for processing into the reporting databases through the Kakfa Change Feed, or triggering asynchronous business rules in the Celery queue.
The data processing service is flexible to store any content sent or received via mobile form submissions or SMS services as long as it adheres to the XForms specification. It also saves all logging and auditing information necessary for data security compliance. The data processing service saves all data at the transactional level so that histories can be audited and reconstructed if necessary.
Synchronization
The synchronization process allows for case and user data to be kept up-to-date through incremental syncs of information from the backend server for offline use cases. To ensure consistency, the backend keeps a shadow record of each user’s application state hashed to a minimal format, when users submit data or request synchronization, this shadow record hash is kept up to date to identify issues with what local data is on device.
Syncs request a diff from the server by providing their current hashed state and shadow record token. The server then establishes what cases have been manipulated outside of the local device’s storage (along with reports or other static data) which may be relevant to the user, such as a new beneficiary or household registered in their region. After all of those cases are established, the server produces an XML payload similar to the ones generated by filling out forms on the local device, which is used to update local device storage with the new data.
Tenant Management Layer
Project Spaces
Every project has its own site on CommCare HQ. Project spaces can house one, or more than one inter-related applications. Data is not shared among project spaces.
Content can be centrally managed with a master project space housing a master application that can be replicated in an unlimited number of additional project spaces. CommCare enables fine grained release management along with roll-back that can be controlled from each project space. These project spaces can be managed under an Enterprise Subscription that enables centralized control and administration of the project spaces.
User Management
There are two main user types in CommCare: Project Users and Application Users.
Project Users are meant to view data, edit data, manage exports, integrations, and application content. Project Users can belong to one or more project spaces and are able to transition between project spaces without needing to login/logout by simply selecting from a drop-down.
Application Users are expected to primarily use CommCare as an end-user entering data and driving workflows through an application.
Project Users and Application Users are stored with separate models. These models include all permission and project space membership information, as well as some metadata about the user such as their email address, phone number, etc. Additionally, authentication stubs are synchronized in real time to SQL where they are saved as Django Users, allowing us to use standard Django authentication, as well as Django Digest, a third-party Django package for supporting HTTP Digest Authentication.
Device and Worker Monitoring
Mobile devices which are connected to the CommCare server communicate maintenance and status information through a lightweight HTTP ‘heartbeat’ layer, which receives up-to-date information from devices like form throughput and application health, and can transmit back operational codes for maintenance operations, allowing for remote management of the application directly outside of a full-fledged MDM.
Analytics and Usage
There are several standard reports available in CommCare. The set of standard reports available are organized into four categories: Monitor Workers, Inspect Data, Messaging Reports and Manage Deployments.
Monitor Workers
Includes reports that allow you to view and compare activity and performance of end workers against each other.
Inspect Data
Reports for finding and viewing in detail individual cases and form submissions.
Messaging Reports
Domains that leverage CommCare HQ’s messaging capabilities have an additional reporting section for tracking SMS messages sent and received through their domain
Manage Deployments
Provides tools for looking at applications deployed to users’ phones and device logging information.
User Defined Reports
In addition to the set of standard reports users may also configure reports based on the data collected by their users. This reporting framework allows users to define User Configurable Reports (UCR) which store their data in SQL tables.
Mobile Reports
UCRs may also be used to send report data to the mobile devices. This data can then be displayed on the device as a report or graph.
Messaging Layer
CommCare Messaging integrates with a SMS gateway purchased and maintained by the client as the processing layer for SMS messages. This layer manages the pipeline from a Case transaction to matching business logic rules to message scheduling and validation.
Conditional Scheduled Messages
Every time a case is created, updated, or closed in a form it is placed on the asynchronous processing queue. Asynchronous processors review any relevant business logic rules to review whether the case has become (or is no longer) eligible for the rule, and schedules a localized message which can contain information relevant to the case, such as an individual who did not receive a scheduled visit.
Broadcast Messages
Broadcast messaging is used to send ad-hoc messages to users or cases. These messages can either be sent immediately, or at a later date and time, and can also be configured to send to groups of users in the system.
Gateway Connectivity and Configuration, Logging, and Audit Tracking
All SMS traffic (inbound and outbound) is logged in the CommCare Message Log, which is also available as a report. In addition to tracking the timestamp, content, and contact the message was associated with, the Message Log also tracks the SMS backend that was used and the workflow that the SMS was a part of (broadcast message, reminder, or keyword interaction).
The messaging layer is also used to provide limits and controls on messaging volume, restricting the number of messages which can be sent in a 24hr period, and restricting the time of day which messages will be sent, to comply with regulations. These restrictions may apply to both ad-hoc and scheduled messages. Messages are still processed and queued 24hrs per day, but only submitted when permitted.
Messaging Dashboards
Charts and other kinds of visualizations are useful for getting a general overview of the data in your system. The dashboards in CommCare display various graphs that depict case, user, and SMS activity over time. These graphs provide visibility into when new cases and users were created, how many SMS messages are being sent daily, and the breakdown of what those messages were used for (reminders, broadcasts, etc.).
Integration
CommCare has robust APIs as well as a MOTECH integration engine that is embedded in CommCare. APIs allow for direct programmatic access to CommCare. The MOTECH integration engine allows for custom business rules to be implemented that allow for real-time or batch integration with external systems. This engine does not have an application or content management environment, and so requires custom engineering to be added to a CommCare instance.
APIs
CommCare has extensive APIs to get data in and out for bidirectional integration with other systems. This method of data integration requires familiarity with RESTful HTTP conventions, such as GET and POST and url parameters.
There are APIs both for reading and writing data to CommCare. This can be updated data related to forms or cases in the system and enable highly-sophisticated integrations with CommCare.
More details on CommCare’s API can be found in the API documentation.
MOTECH Repeaters
For interoperability with external systems which process transactional data, CommCare has a MOTECH repeater layer, which manages the pipeline of case and form transactions received and manages the lifecycle of secure outbound messages to external systems.
This architecture is designed to autonomously support the scale and volume of transactional data up to hundreds of millions of transactions in a 24hr period.
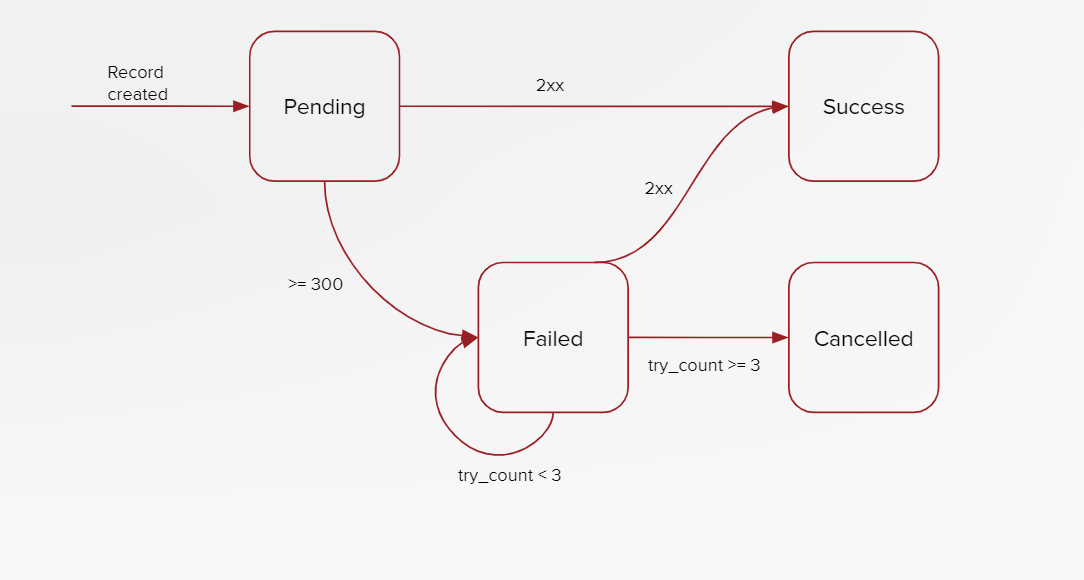
New transformation code for this subsystem can be authored as Python code modules for each outbound integration. These modules can independently transform the transactional data for the repeater layer, or rely on other data from the application layer when needed by integration requirements.